Check Out Our Recent Video on SCHD:
Overview of SCHD
The Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) is a popular ETF in the domain of dividend-focused investment solutions, focused on delivering stable, high-yield payouts alongside the potential for capital appreciation. Established by Charles Schwab in 2011, SCHD tracks the Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index, comprising 100 high-dividend-yielding stocks selected rigorously based on their financial health and sustainability. This criteria guarantees that the fund invests exclusively in companies which boast a solid history of dividend payments, along with solid fundamentals.
Purpose of the Article
This article is focused on exploring SCHD on a deep level, offering a detailed review of its investment strategy, performance metrics across various market conditions, associated risk factors, and its role within a diversified investment portfolio. By taking a close look at these factors, the hope is that you will have a better understanding of SCHD as it relates to a possible ETF which can be used as a reliable, income focused investment vehicle.
Relevance to Investors
In the current economic landscape continually marked by volatility and higher interest rates, there are many different things to consider when it comes to choosing the specific assets and investment vehicles for your portfolio(s). Dividend-paying stocks, especially those constituting SCHD’s portfolio, are known to offer:
- Stability and Predictability: Regular dividends ensure a consistent income stream and help mitigate portfolio volatility.
- Inflation Protection: Companies with a track record of consistent dividend increases can help keep pace with inflation, thereby safeguarding your capital’s purchasing power.
- Performance Across Market Conditions: Historically, dividend-yielding stocks have shown robust performance through various market cycles, particularly in environments with rising interest rates, where bonds may falter, due to the inverse rate relationship.
As interest rates remain elevated, the allure of dividend ETFs such as SCHD remains as a strategic choice if you’re an investor who is seeking a regular income stream, along with a defensive posture against market uncertainty and volatility.
Detailed Exploration of SCHD
Investment Strategy
SCHD’s strategy to track the Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index involves selecting companies that are not only leading in terms of dividend yield, but additionally exhibit financial robustness and sustainability. This dual focus ensures that the investments are secure, profitable, and capable of sustaining dividends throughout various economic conditions.
Criteria for Selection:
- Dividend Yield: Companies must qualify a minimum threshold for dividend yield.
- Financial Health: Metrics such as debt-to-equity ratio, return on equity, and free cash flow are analyzed to assess a company’s financial stability.
- Sustainability: The ability of companies to maintain and potentially increase dividend payouts without compromising their financial health is considered.
Performance Metrics
Analyzing SCHD’s performance involves looking at its historical yield, total return, and performance stability during market downturns.
- Historical Performance: Since its inception, SCHD has consistently provided yields that are competitive with higher yielding dividend stocks, while maintaining lower volatility. For example, the current beta of SCHD is .89, indicating it is less volatile than the S&P 500 on average. Additionally, the current dividend yield of 3.46% is attractive if you’re an investor seeking a regular income stream, and lower volatility.
- Total Return: SCHD is up 5.36% over the last year, not accounting for any dividends (just share price).
- Market Downturns: SCHD’s strategy is focused on ensuring that it remains less volatile during market downturns, providing investors with a relatively stable income option.
Risk Factors
Investing in SCHD, like any investment, involves certain risks. These include sector concentration risks, where too much exposure to specific sectors can affect performance during sector downturns, and market risk, where overall market declines can reduce asset values irrespective of individual stock performance. Below are a couple of risks to consider, although this list is not exclusive, and there are many other risks (both systemic and non-systemic) that may be relevant to this ETF:
- Interest Rate Risk: Rising interest rates can particularly impact dividend-paying stock prices negatively.
- Economic Sensitivity: Some sectors within SCHD may be more sensitive to economic changes than others, affecting their stock prices and the overall performance of the ETF.
Role in Diversified Portfolio
Incorporating SCHD within a diversified portfolio can enhance your overall income, while reducing the beta or overall volatility in your portfolio. Its role can be particularly strategic in balancing a portfolio which may be heavily invested in growth stocks or bonds.
Let’s Discuss Further
The Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) presents itself as an interesting solution if you’re an investor who is aiming to capitalize on consistent dividend payments, with the added potential for capital appreciation. Its strategic focus on financially healthy and sustainable companies makes it an attractive option for generating steady income while mitigating investment risks associated with market volatility and economic downturns.
Section 1: Fundamentals of SCHD
Fund Overview
Fund Basics:
- Ticker: SCHD
- Inception Date: October 20, 2011
- Issuer: Charles Schwab Investment Management
As we discussed above, the SCHD ETF is tailored if you’re an investor who is seeking a dependable source of income through dividends, combined with the potential for capital gains by tracking a selection of high-yield dividend stocks noted for their financial robustness and sustainability.
Investment Strategy
Index Tracked:
Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index
SCHD meticulously follows this index, which aims to reflect the performance of 100 leading dividend-paying U.S. companies. These companies are not only industry leaders, but also exhibit a consistent dividend distribution history.
Selection Criteria:
- High Dividend Yielding Stocks: The ETF predominantly invests in companies that offer higher dividend yields relative to their industry peers, which typically indicates a solid financial foundation that supports sustainable dividend payouts.
- Consistency in Dividends: It includes companies that have managed to increase or maintain their dividend for at least ten consecutive years, ensuring inclusion of only those with a reliable track record of shareholder returns.
- Future Sustainability: The sustainability of dividends is also a key factor, assessed by examining each company’s payout ratio, free cash flow, and debt-to-equity ratios. This ensures that the dividends are not only attractive but also maintainable in the long run.
Portfolio Composition:
Sectors Represented:
The ETF is well-diversified across various sectors, prominently focusing on some of the following sectors:
- Consumer Staples
- Financials
- Information Technology
- Health Care
This sectoral diversification is strategic, which helps to mitigate risks which may be specific to any single industry, while additionally exploiting some of the various strengths across different areas of the economy.
Top Holdings:
Among the top companies included in the ETF are firms such as Texas Instruments, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lockheed Martin, PepsiCo, Cisco Systems, and many other well-established brands. These companies are celebrated not just for their market leadership, but also for their consistent and reliable dividend distributions.
Allocation Strategy:
The fund’s allocation to each stock is carefully calculated, taking into consideration factors like the stock’s yield, consistency in dividend payments, and the sustainability of these dividends. This ensures that the overall portfolio is not only high-yielding, but also balanced in terms of risk and return.
Performance Indicators:
- Yield and Total Return: SCHD is often favored for its higher yield compared to broader market indices, which is particularly appealing if you’re an income-focused investor, who also wants to participate in some of the upside of the broad stock market.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns: By focusing on high-quality, dividend-paying stocks, SCHD generally delivers superior risk-adjusted returns compared to its peers. This aspect is especially valued if you are an investor who is seeking stability in addition to growth.
Section 2: Performance Analysis
Understanding the performance dynamics of the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) involves a detailed look at its dividend payouts, price performance across economic cycles, and the efficiency brought by its low expense ratio. These factors collectively contribute to its appeal as a high-yield, stable investment vehicle, suitable (once again) if you’re an investor who is aiming for both income and moderate capital appreciation.
Dividend Analysis
Historical Dividend Yields:
- Yield Trends: Historically, SCHD has been among the top dividend-yielding ETFs in its category, consistently offering yields between 3% and 4%. This is significantly higher than the typical yields offered by broader indices such as the S&P 500, which have hovered around 1.5% to 2%. This high yield is a direct result of its strategic holdings in sectors known for higher dividend payouts.
- Sector Comparison: SCHD’s focus on sectors like Consumer Staples and Utilities, which traditionally feature higher-than-average dividend yields, positions it well during market volatility when investors might seek safer, income-generating stocks. These sectors not only provide stability but also tend to outperform in terms of yield during economic downturns.
Payout Frequencies:
- Quarterly Distributions: Aligning with industry norms, SCHD pays out dividends quarterly, or every three months.
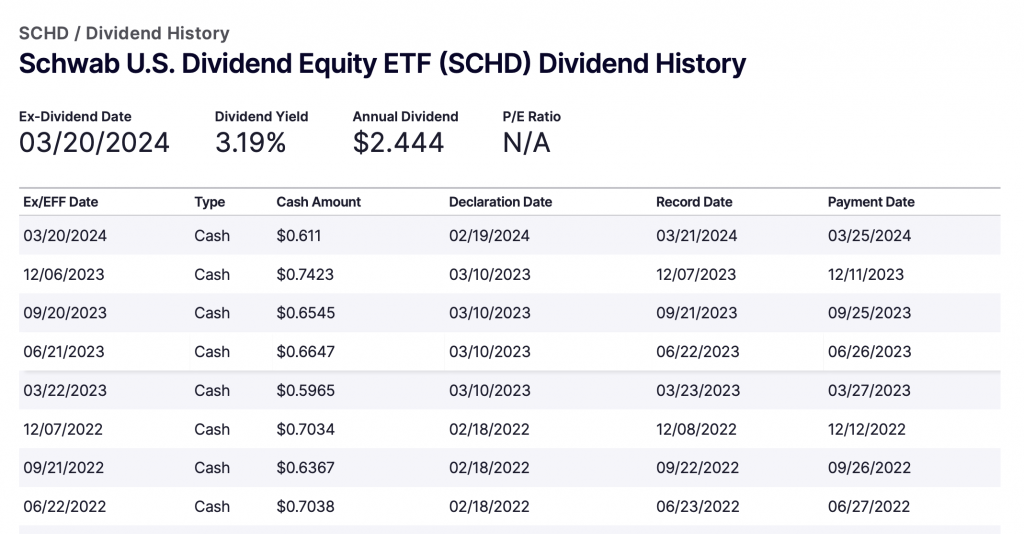
- Most Recent Dividends: The most recent dividend payouts, as can be seen below in the picture courtesy of Nasdaq.com, include $0.611, $0.7423, $0.6545 and $0.6647, with an annual dividend of $2.444.
Price Performance
Market Adaptability:
- Economic Cycles: SCHD has demonstrated resilience across varying market conditions. Notably, during downturns like those in late 2018 and early 2020, SCHD’s investment in less volatile, high-dividend stocks has often led to outperformance relative to broader markets.
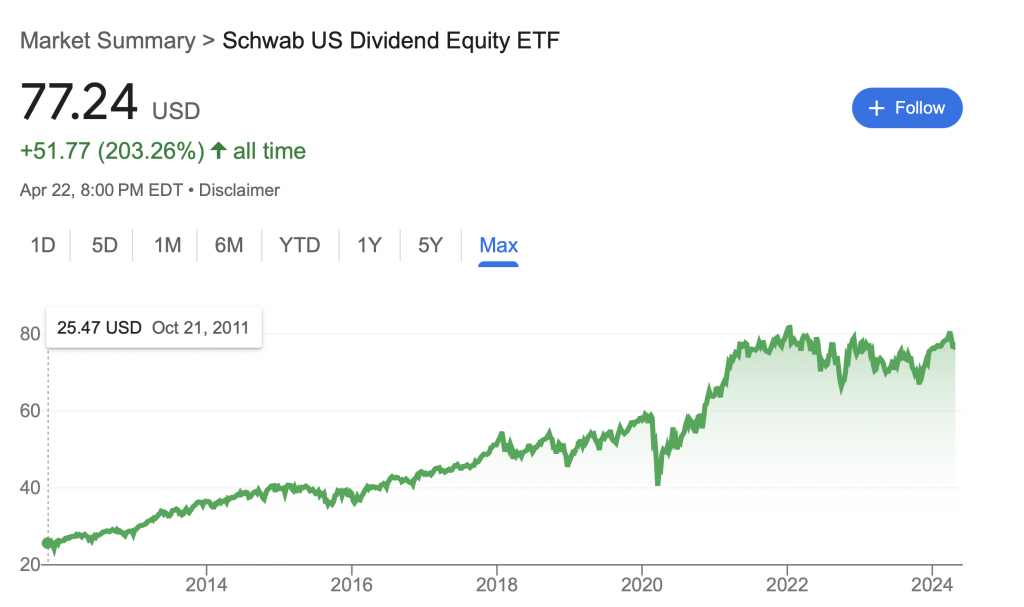
- Recovery Phases: In contrast, during bull markets, SCHD’s conservative, defensive positioning might limit its upside potential compared to indices that include growth-oriented stocks without dividend focus. However, it still participates in some of the upside of the major indexes, reflecting a balanced risk management approach. Since inception in 2011, the ETF is up more than 200%, not including dividends:
Comparison to Benchmark:
- Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index: SCHD closely tracks its benchmark index with minimal tracking errors.
- Other Benchmarks: Compared to the S&P 500, SCHD typically offers a higher yield but might lag in total return during strong growth phases, due to its composition predominantly of slower-growing, high-dividend companies. SCHD’s beta is a consideration, since there is less volatility than the S&P 500, and therefore one can expect lower total returns.
Expense Ratio
Cost Efficiency:
- Expense Ratio Analysis: At just 0.06%, SCHD’s expense ratio is one of the lowest in its class, which significantly enhances its attractiveness by reducing the cost drag on investment returns.
- Comparison with Peers: SCHD’s expense ratio undercuts many competitors, where similar dividend-focused ETFs may charge between 0.08% and 0.40%. This cost efficiency is particularly beneficial over the long term, as it can allow you to retain a larger portion of the returns generated.
Impact on Returns:
- Long-Term Effects: The compounding effect of the lower expense ratio becomes more pronounced over longer periods. This is due to the fact that a lower expense ratio equates to less money spent on fees, and the compounding effect is more pronounced over the long-term.
- Illustrative Example: Considering a $10,000 investment over 10 years at an average return rate of 6%, the difference between paying a 0.06% expense ratio (SCHD) versus a 0.30% ratio (peer) can save an investor approximately $440, assuming the compound interest is calculated annually. This difference highlights the impact of lower fees on investment growth.
Conclusion of Performance Analysis
SCHD’s strategic investment choices, focusing on high-yield, financially solid companies, combined with its cost-efficiency and consistent performance across various market conditions, make it a choice of consideration if you are an investor who prioritizes income alongside stability.
In the following section, we will explore SCHD’s comparative advantages relative to similar funds, further detailing its suitability within a diversified portfolio, and strategic fit for various investment approaches.
Section 3: Comparative Analysis & Suitability
SCHD vs. Other Dividend ETFs
In the world of dividend-focused ETFs, SCHD (Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF) competes closely with other prominent players such as VYM (Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF) and HDV (iShares Core High Dividend ETF). Each of these funds has distinct characteristics which are tailored to different investor needs, which warrants a detailed comparison to understand SCHD’s relative positioning.
ETF Comparisons:
1. VYM (Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF):
- Index Tracked: VYM follows the FTSE High Dividend Yield Index, which is designed to reflect the performance of U.S. stocks that exhibit high dividend yields.
- Yield Profile: It typically offers a higher yield by focusing exclusively on high dividend-paying companies, making it attractive for yield-seeking investors.
- Portfolio Composition: VYM is more diversified across various sectors, but places less emphasis on the financial health of the companies included, which may introduce higher risk levels.
2. HDV (iShares Core High Dividend ETF):
- Index Tracked: HDV tracks the Morningstar Dividend Yield Focus Index, consisting of U.S. equities that are financially healthy, and have the potential for high dividend yields.
- Yield Profile: Generally, HDV provides a yield comparable to SCHD, with a strong emphasis on sustainability and quality of dividends.
- Portfolio Composition: Similar to SCHD, HDV focuses on value stocks with solid financial health metrics, making it a close competitor in terms of investment philosophy.
Investor Suitability:
Now, let’s take a deeper look at what types of investors may be suitable for SCHD:
Retirees Seeking Reliable Income:
- SCHD may be suitable if you are a retiree or are nearing retirement, since it prioritizes a consistent and reliable income stream. Its emphasis on dividend sustainability ensures that payouts grow over time, keeping pace with inflation and preserving value.
Long-Term Investors Focusing on Steady Growth:
- If you are an investor who is focused on a long-term horizon, you may find SCHD appealing due to its balanced approach to income generation and capital appreciation. The ETF’s focus on financially robust companies likely to increase dividends offers a prudent path to wealth accumulation.
Risk-Averse Investors:
- Additionally, if you are more on the conservative side or are simply focused on diversifying away from high-volatility sectors, you may appreciate SCHD’s stable return profile, which is backed up by solid company fundamentals, and a strategic focus on dividend growth and sustainability.
Section 4: Risk Assessment
Understanding the inherent risks associated with investing in the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) is essential to make informed decisions. This section will explore the key factors contributing to SCHD’s volatility, along with the economic impacts that could influence its performance.
Market Risks
Volatility Factors:
1. Market Sentiment and Investor Behavior:
- Cyclicality: While SCHD’s investments in consumer staples (considered defensive) tend to be less sensitive to economic cycles, its substantial allocations in more cyclical sectors such as industrials and financials can introduce greater volatility during economic shifts.
- Investor Reaction: During periods of market stress, investors’ flight to or from dividend stocks, depending on their risk perception, can significantly impact SCHD’s price due to its dividend-focused nature.
2. Dividend Payment Adjustments:
- Company Performance: If key companies within SCHD’s portfolio reduce or eliminate their dividends, it could trigger a substantial price drop in the ETF, as its performance is tightly linked to the stability and reliability of its dividend payments.
- Sector Health: Fluctuations in sector conditions, especially in significant areas such as healthcare and financials, due to regulatory or economic changes, can impact the dividend disbursement capabilities of these companies, thus impacting SCHD.
3. Interest Rate Fluctuations:
- Rate Increases: Typically, rising interest rates make bonds more appealing compared to dividend stocks, which might prompt a sell-off or under performance in dividend-focused ETFs such as SCHD.
- Yield Relationship: As bond yields rise, the relative attractiveness of dividend stocks may decline, unless these stocks can proportionately increase their dividends to match rising bond yields.
Economic Impacts
Effects of Economic Downturns, Interest Rate Changes, and Inflation:
1. Economic Downturns:
- Defensive Positioning: SCHD’s emphasis on high-quality, reliable dividend payers can provide a buffer against harsh economic downturns, as these entities are more likely to maintain dividend payouts.
- Recession Resilience: Companies within SCHD’s portfolio typically boast strong financials with solid balance sheets and consistent earnings, positioning them to better withstand economic recessions.
2. Interest Rate Changes:
- Negative Correlation: SCHD and similar dividend-focused investments generally exhibit an inverse performance relationship to interest rate rises. As rates climb, the increasing yields of fixed-income alternatives might become more attractive.
- Capital Costs: Higher interest rates can raise capital costs, which might compress the profits of companies with high debt levels, adversely impacting their ability to sustain dividends.
3. Inflation Impacts:
- Eroding Purchasing Power: Inflation can diminish the actual returns of dividends unless companies can increase their dividends accordingly.
- Cost Pressures: Firms in SCHD’s portfolio facing heightened costs due to inflation may see squeezed profit margins, which could inhibit their dividend growth potential.
Conclusion
While SCHD is designed to offer relative stability through its focus on dividends, it is not devoid of market volatility risks. Economic downturns, sector-specific developments, interest rate fluctuations, and inflationary pressures are all important factors that can impact its performance. If you are considering this ETF, you should carefully evaluate these risks in conjunction with SCHD’s potential benefits, such as higher dividend yields, and defensive posturing.
Section 5: Investment Suitability:
Strategic Portfolio Integration
Investing in the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) requires strategic considerations to align with your investment goals. This section will detail effective methods for incorporating SCHD within your own diversified investment strategy, highlighting its synergistic potential with other asset classes.
Recommendations on Integrating SCHD:
Foundation for Income and Growth:
- Core Holding: SCHD is ideally suited as a core equity holding in any portfolio, particularly if you are focused on generating steady income, while still benefiting from potential capital appreciation. Its investments in high-dividend-yielding, financially robust companies make it a dependable source of passive income.
- Diversification: Although SCHD is diversified across various sectors, incorporating it alongside other asset classes such as bonds, international stocks such as emerging markets, or alternative investments can enhance overall portfolio diversification, reduce risk, and potentially increase returns.
Risk Management:
- Volatility Buffer: Due to its lower beta relative to broad market indexes, SCHD is considered less volatile than the overall stock market, making it an excellent option for stabilizing portfolio performance in fluctuating markets.
- Counterbalance to Cyclicals: For portfolios heavily invested in cyclical sectors or growth-focused stocks, SCHD can provide a stabilizing counterbalance, thanks to its defensive sector allocations (such as consumer staples and utilities) which perform reliably across economic cycles.
Allocation Guidelines:
- Conservative Portfolios: If you are a risk-averse investor, SCHD could represent 20-30% of the equity portion, given its low volatility and stable dividend payouts.
- Aggressive Portfolios: If you are seeking higher growth yet are still looking to lower volatility in your portfolio, perhaps an allocation of 10-15% to SCHD would be appropriate.
Synergies with Other Investments
How SCHD Complements Other Investment Vehicles:
With Bonds:
- Yield Enhancement: In environments where traditional bonds offer diminished returns, particularly during periods of low interest rates, SCHD can enhance a portfolio’s yield profile without correspondingly increasing its risk exposure.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity Buffer: With its focus on dividends rather than price appreciation, SCHD exhibits less sensitivity to interest rate hikes than long-duration bonds, making it a prudent complement in a mixed-asset portfolio.
With International Stocks:
- Geographic Diversification: Combining SCHD with international equities can broaden the geographic diversity of a portfolio, reducing vulnerability to U.S.-specific economic downturns and tapping into growth opportunities in emerging markets.
- Currency Risk Mitigation: While international investments introduce currency risk, pairing them with U.S.-focused income-generating assets like SCHD can offset some of these risks, providing a more balanced currency exposure.
With Growth-Oriented Equities:
- Growth and Income Balance: Integrating SCHD with sectors known for rapid growth but low dividends, such as technology or biotech, offers a balanced approach, combining high potential for capital gains with stable dividend income.
- Sector Complementarity: SCHD’s focus on traditionally less volatile sectors complements investments in high-volatility areas, providing continuous income during periods when growth stocks might underperform.
Conclusion
Summary of SCHD’s Attributes
The Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD) emerges as a potentially solid choice if you are an investor who may be seeking reliable dividend income, combined with opportunities for moderate capital appreciation. Below we recap some of the primary things to consider with this ETF:
Key Benefits:
- Stable Dividend Income: SCHD strategically targets companies that not only offer high dividend yields, but also showcase a history of dividend stability and growth. This makes it an excellent source for steady, reliable income.
- Quality Focus: By adhering to stringent selection criteria that emphasize profitability, consistent dividend yields, and solid financial health, SCHD invests exclusively in high-quality companies.
- Risk Management: SCHD’s focus on quality dividend-paying stocks generally results in lower volatility compared to broader market ETFs, making it a safer option during economic uncertainties.
- Sector Diversification: Although SCHD has substantial allocations in stable sectors like consumer staples and utilities, it also covers sectors like information technology and financials, which broadens its market scope and enhances diversification.
Considerations:
- Capped Growth Potential: Given its high dividend yield focus, SCHD may offer modest growth potential compared to growth-centric funds. This inverse relationship between dividend yield and capital appreciation is an important consideration.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: While SCHD is less sensitive to interest rate changes than bonds, significant rate shifts can still impact the attractiveness of dividend-paying stocks, potentially impacting the ETF’s performance.
Final Recommendations
Tailored Advice for Different Investor Profiles:
- Retirees and Income-Focused Investors: SCHD is ideal if you are a retiree or seeking a regular income stream, due to its emphasis on high, stable dividend yields and lower overall volatility.
- Long-Term Investors: If you’re an investor who has an extended time horizon, you may benefit from the compounding effects of SCHD’s reinvested dividends and the capital appreciation potential of its quality stock holdings.
- Risk-Averse Investors: If you are cautious about market dips, you may value SCHD’s conservative investment approach, which focuses on stable sectors and financially sound companies, mitigating large value fluctuations.
- Growth and Income Investors: If you are seeking to balance between income and growth, SCHD can serve as a foundational income component, allowing room for allocation to riskier, high-growth investments within a diversified portfolio.
Call to Action
Integrating SCHD Into Your Investment Strategy:
- Consult a Financial Advisor: Before adjusting your portfolio to include SCHD, consulting with a financial advisor can help refine your strategy based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
- Further Research: Diligent research or discussions with investment professionals are recommended to fully grasp how SCHD might fit into your broader investment strategy and complement other portfolio components.
- Diversification Strategy: Assess how SCHD can diversify risk across your investment portfolio. Its stability and consistent dividend payouts provide a counterbalance to portfolios concentrated in volatile, high-growth assets.
Incorporating SCHD can significantly enhance your portfolio’s income capabilities while providing exposure to stable, high-quality U.S. equities. Its deliberate approach to dividend investing, characterized by selecting financially robust companies, offers a compelling investment case for those who value a blend of income generation and moderate capital growth.




